Custom reports
Koha’s data is stored in a MySQL database which means that librarians can generate nearly any report they would like by either using the guided reports wizard or writing their own SQL query.
Add custom reportNote
Only staff with the create_reports permission (or the superlibrarian permission) will be able to create custom reports, either with the guided report wizard or directly with SQL.
The guided report wizard will walk you through a six step process to generate a report.
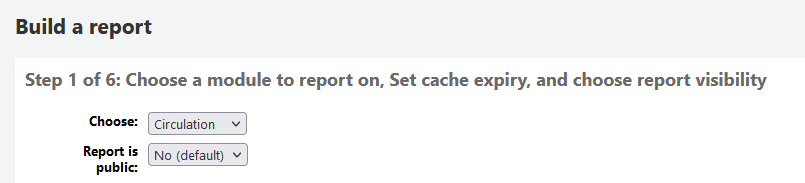
Step 1: Choose the module you want to report on. This will determine what tables and fields are available for you to query.
‘Report is public’ should be left to the default of ‘No’ in most cases especially if the report contains patron or other sensitive information. A public report can be accessed using the JSON reports services by anyone and without authentication.
Note
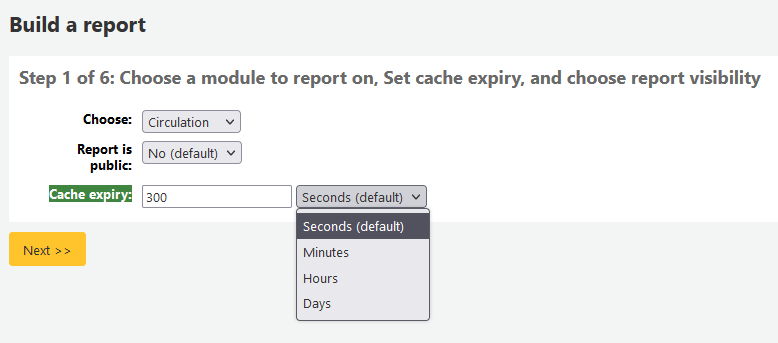
If your system administrator has set up memcache on your server you might see one more option for the Cache expiry. This is related to your public reports. If you make the report public then it’s constantly running and will cause a large load on your system. Setting this value prevents that.
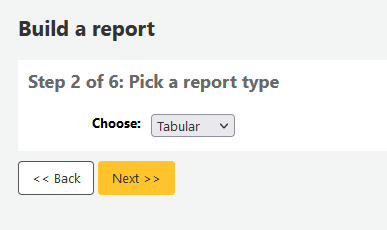
Step 2: Choose a report type. For now, Tabular is the only option available.
Step 3: Choose the fields you want in your report. You can select multiple fields and add them all at once by using CTRL+click on each item you want to add before clicking the Add button.
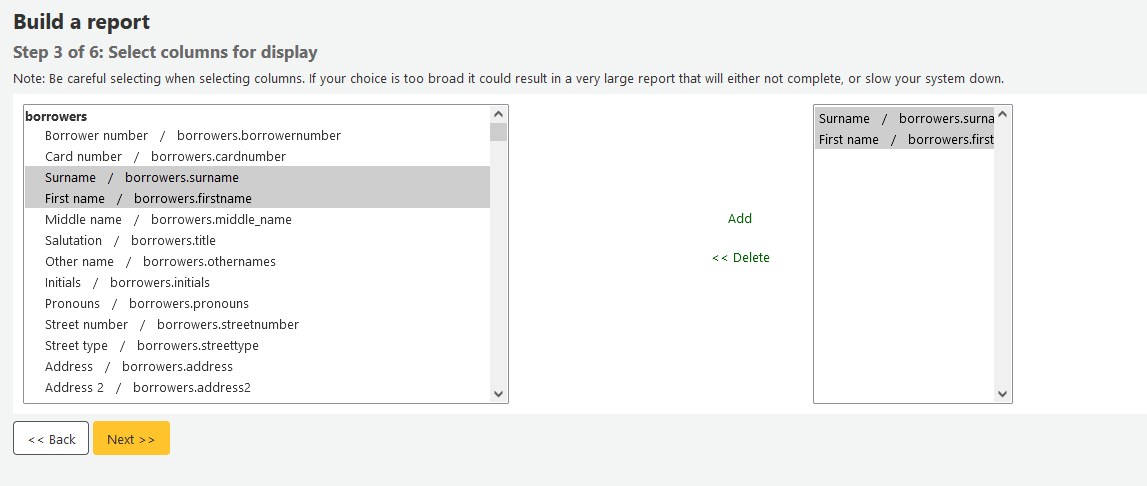
Step 4: Choose any limits you might want to apply to your report (such as item types or branches). If you don’t want to apply any limits, simply click ‘Next’ instead of choosing an option.
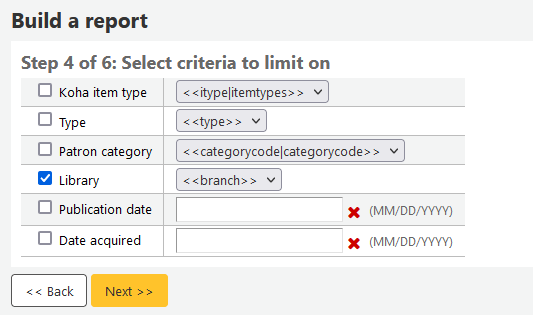
Step 5: Perform math functions. If you don’t want to do any calculations, simply click ‘Next’ instead of choosing an option.
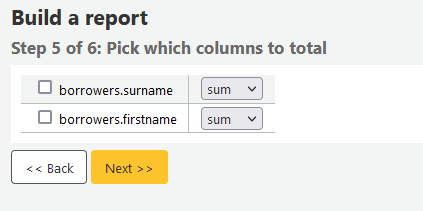
Step 6: Choose data order. If you want the data to print out in the order it’s found in the database, simply click ‘Finish’.
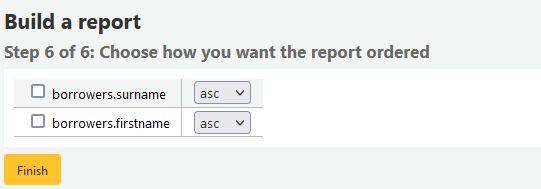
When you are finished you will be presented with the SQL generated by the report wizard. From here you can choose to save the report by clicking ‘Finish’ or copy the SQL and make edits to it by hand.

If you choose to save the report you will be asked to name your report, sort it in to groups and subgroups and enter any notes regarding it.
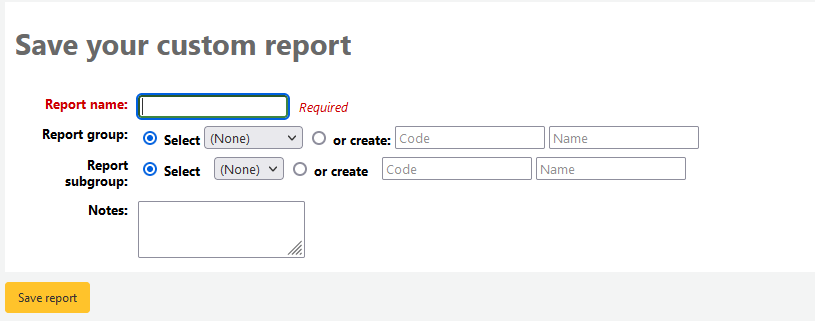
Once your report is saved it will appear on the ‘Use saved’ page with all other saved reports.

Note
You can customize the columns of this table in the ‘Table settings’ section of the Administration module (table id: table_reports).
From here you can make edits, run the report, or schedule a time to have the report run. To find the report you created you can sort by any of the columns by clicking the on the column header (creation date is the best bet for finding the report you just added). You can also filter your results using the filter menu on the left or use the tabs to find reports based on your custom groups.
Report from SQLIn addition to the report wizard, you have the option to write your own queries using SQL. To find reports written by other Koha users, visit the Koha wiki: http://wiki.koha-community.org/wiki/SQL_Reports_Library. You can also find your database structure in /installer/data/mysql/kohastructure.sql or online at: http://schema.koha-community.org.
To add your query, click the link to ‘Create from SQL’ on the main reports module
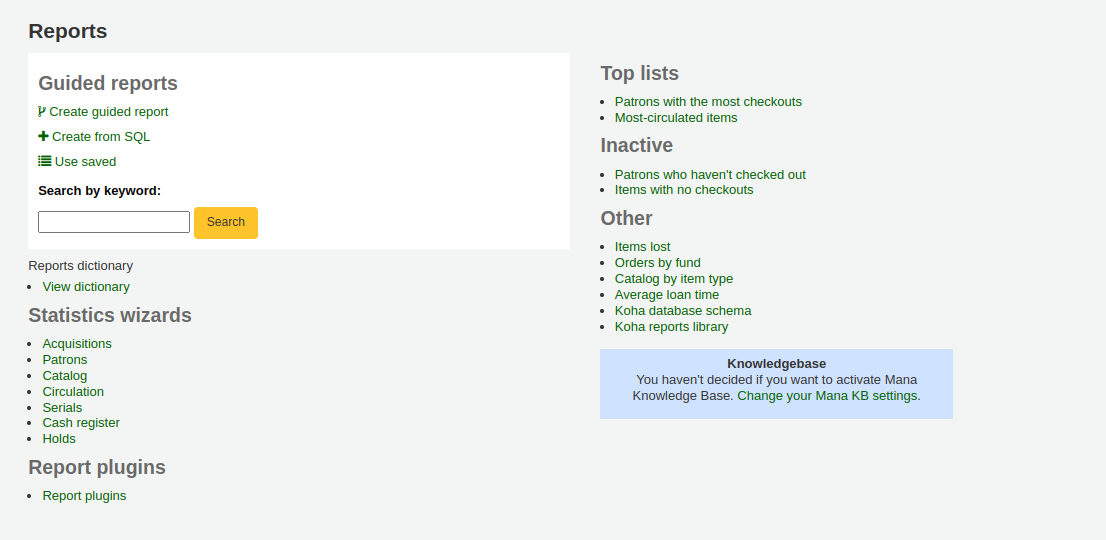
or the ‘New report’ button at the top of the ‘Saved reports’ page.

Fill in the form presented
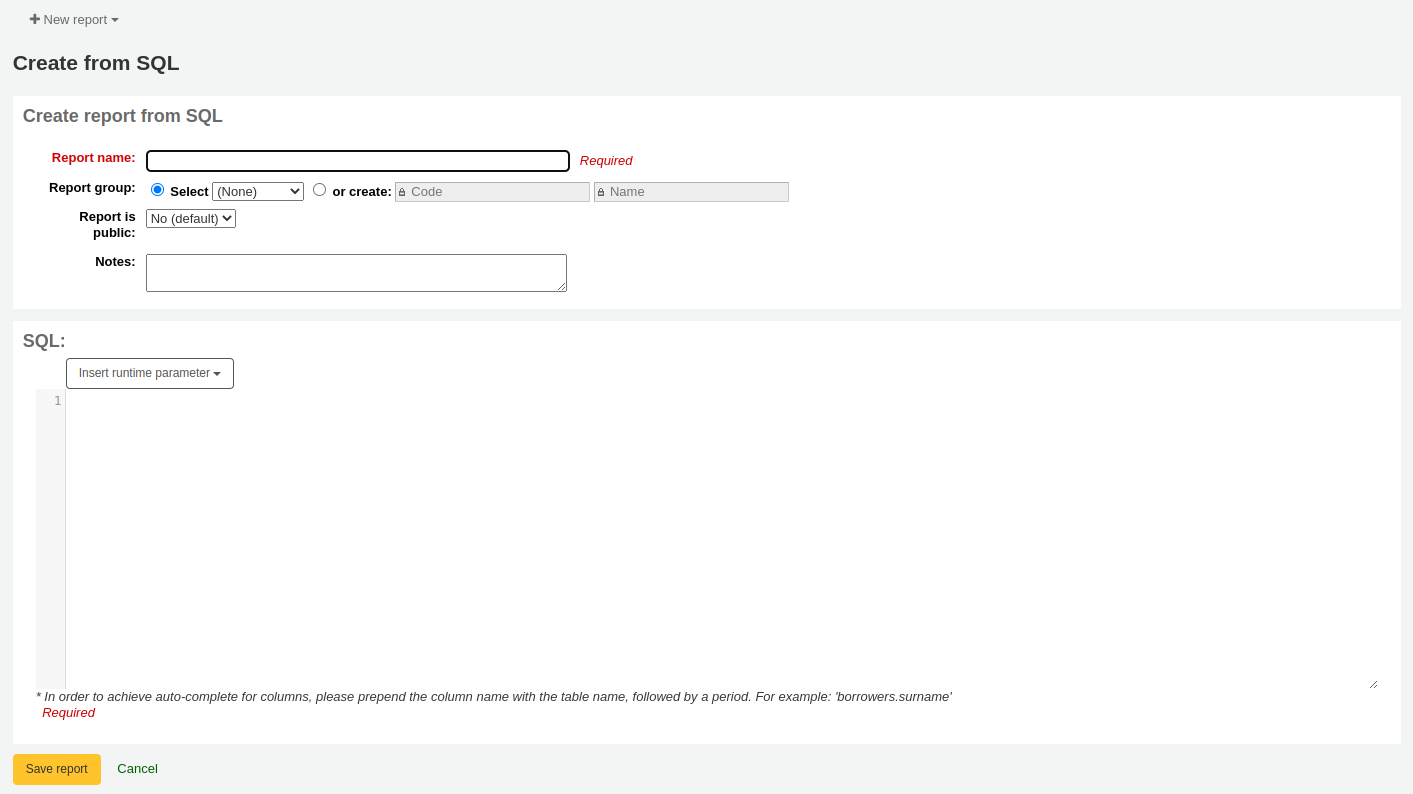
Report name: the name is what will appear on the ‘Saved reports’ page to help you identify the report later. It will also be searchable using the filters found on the left of the ‘Saved reports’ page.
Report group: you can use the ‘Report group’ to organize your reports in tabs on the ‘Saved reports’ page. You can choose from the list of existing groups, or create one on the fly by choosing the ‘or create’ radio button.
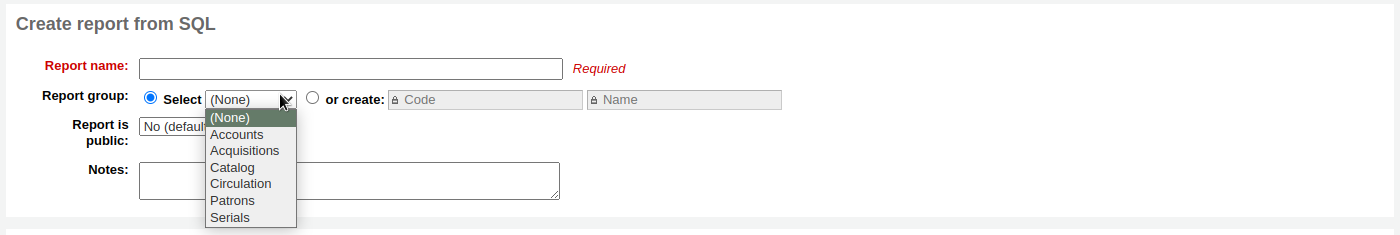
Report groups are set in the REPORT_GROUP authorized value category.
Warning
If you’re adding a report group on the fly, the code should not include special characters or spaces.
Report subgroup: if you chose a report group, this field will appear to further organize your reports. Choose a subgroup from the list, or create one on the fly by choosing the ‘or create’ radio button.
Report subgroups are set in the REPORT_SUBGROUP authorized value category.
Note
Report subgroups need to have unique values in ‘Authorized value’ and ‘Description’. The ‘Description (OPAC)’ field needs to contain the authorized value for the report group that the subgroup falls under.
Warning
If you’re adding a report subgroup on the fly, the code should not include special characters or spaces.
Report is public: this should be left to the default of ‘No’ in most cases, especially if the report contains patron or other sensitive information. A public report can be accessed using the JSON reports services by anyone and without authentication.
Cache expiry: this field will only appear if your system administrator has set up memcache on your server. This is related to public reports. If you make the report public, it’s constantly running and will cause a large load on your system. Setting this value prevents that.
Notes: notes will appear on the ‘Saved reports’ page, and can be used to provide more details about the report or tips on how to enter values when it runs.
SQL: type or paste the SQL for the report (see report writing tips below).
Once everything is entered click the ‘Save report’ button and you’ll be presented with options to run it. From here, you can also edit it, duplicate it, or schedule it to be run later.
Once a report is saved, you do not have to recreate it, it will appear on the ‘Saved reports’ page with all other saved reports.

Note
You can customize the columns of this table in the ‘Table settings’ section of the Administration module (table id: table_reports).
From the ‘Saved reports’ page, you can make edits, run the report, or schedule a time to run the report later. To find the report you created, you can sort by any of the columns by clicking on the column header (creation date is the best to find the report you just added). You can also filter your results using the filter menu on the left or use the tabs to find reports based on your custom groups.
SQL Report writing tips AutocompleteWhen you start typing in the SQL field, autocomplete options will be displayed.
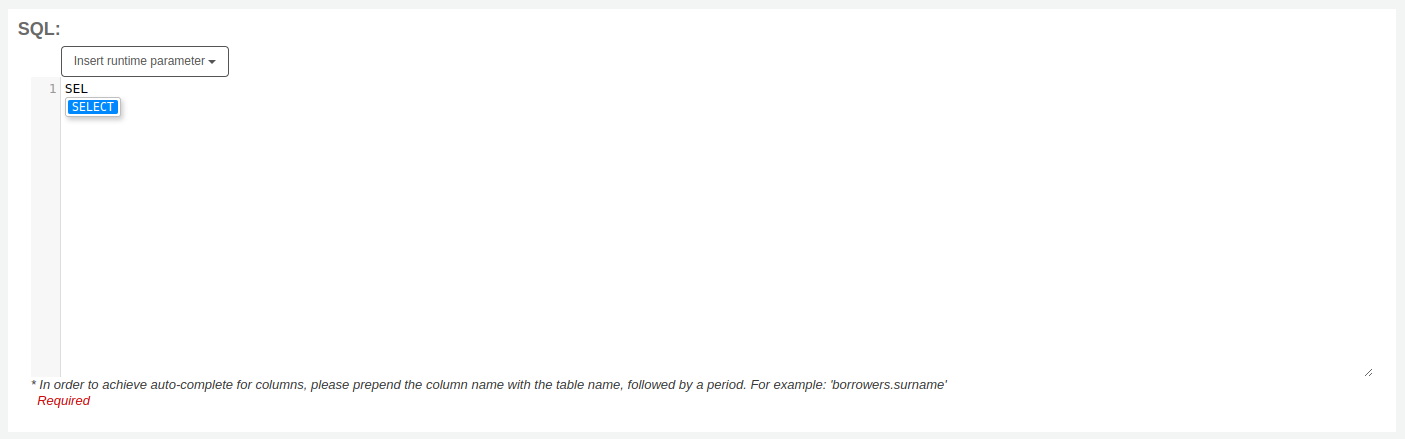
Use the arrows on your keyboard to choose the correct option and press ‘Enter’ or ‘Tab’ to insert it into your report, or simply click on the option to insert it.
Autocomplete options include:
SQL keywords such as SELECT, FROM, WHERE, etc.
table names
column names
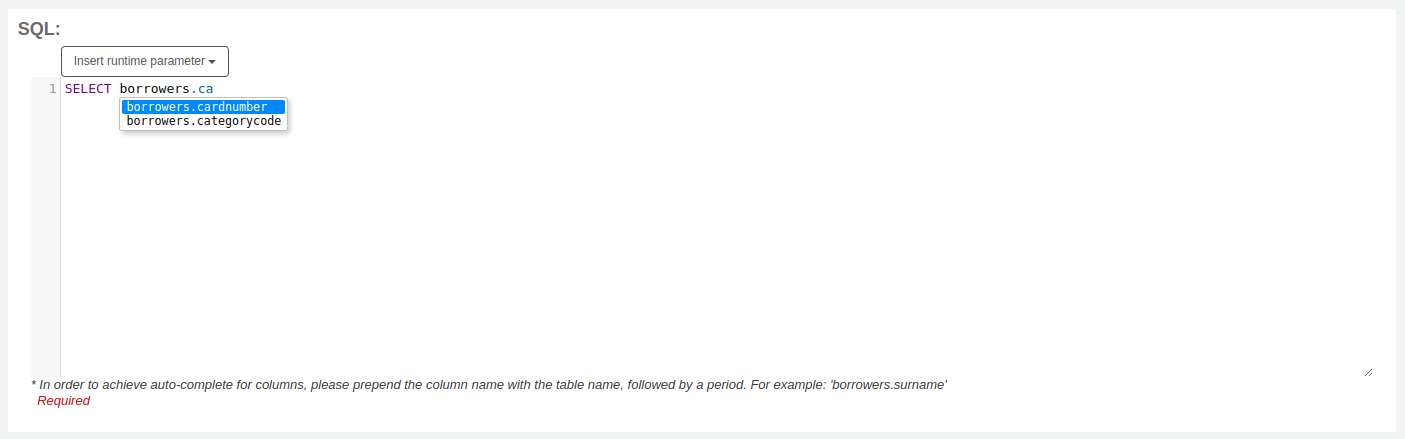
Note
To have suggestions for column names, you must type the table name first, followed by a period, then start typing the column name.
For example, to have the suggestion for cardnumber, you must type borrowers.ca.
If you feel that your report might be too resource intensive you might want to consider using runtime parameters to your query. Runtime parameters basically make a filter appear before the report is run to save your system resources.
Click the button ‘Insert runtime parameter’ and choose which parameter to add.
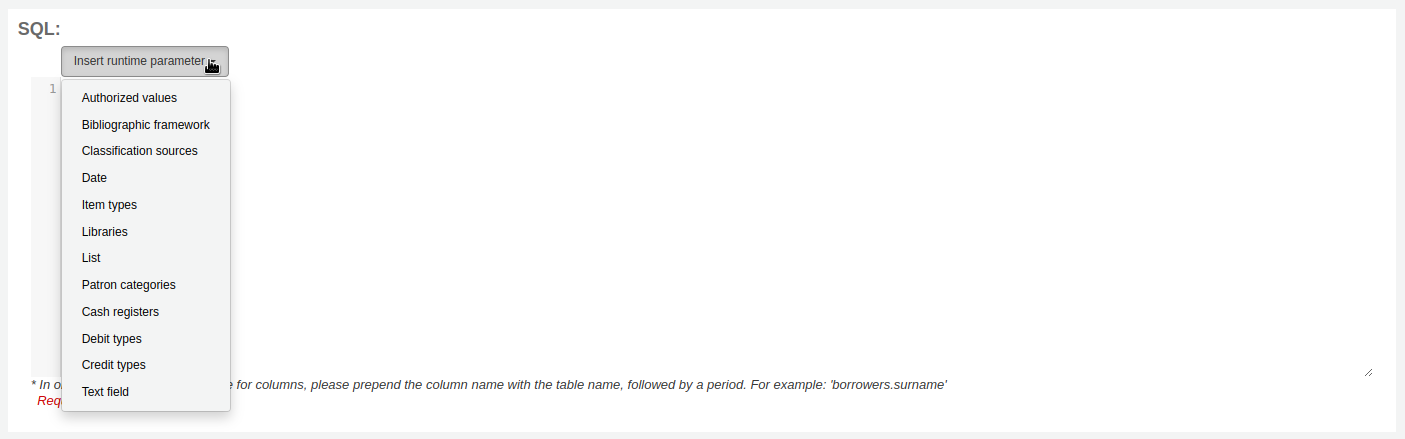
Authorized value: will display a drop down menu of the value descriptions from the chosen authorized value category. The authorized value code will be inserted in the report when it is run.
Bibliographic framework: will display a drop down menu of MARC bibliographic frameworks. The framework code will be inserted in the report when it is run.
Classification sources: will display a drop down menu of classification sources. The classification code will be inserted in the report when it is run.
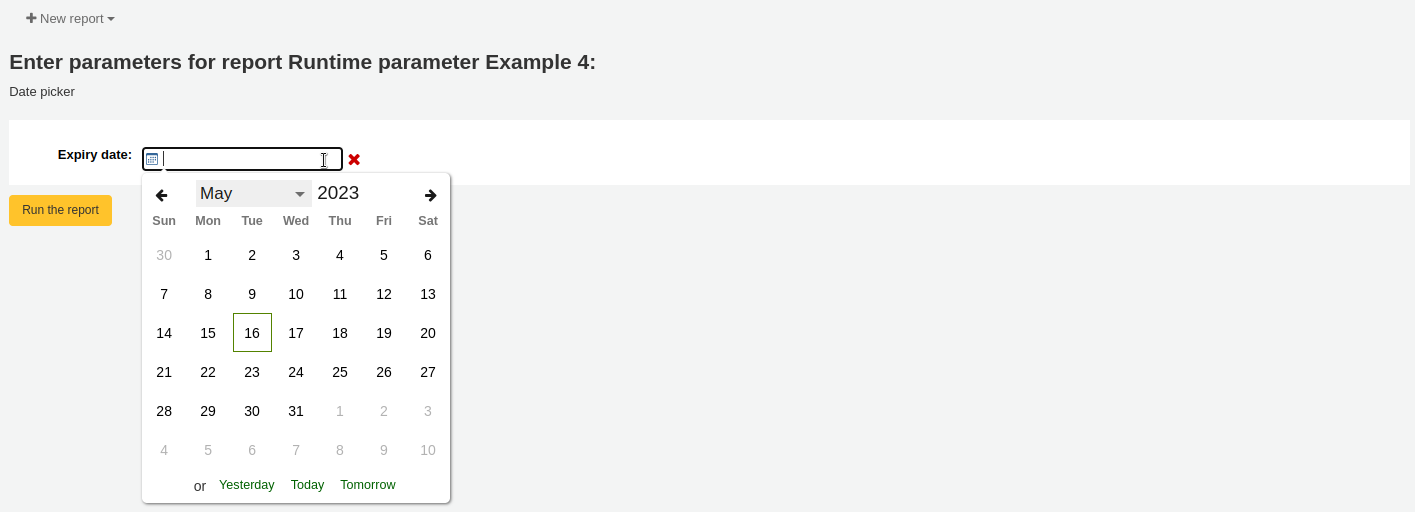
Date: will display a calendar to pick a date. The date in YYYY-MM-DD format will be inserted in the report when it is run.
Item types: will display a drop down menu of item types. The item type code will be inserted in the report when it is run.
Libraries: will display a drop down menu of libraries. The library code (branchcode) will be inserted in the report when it is run.
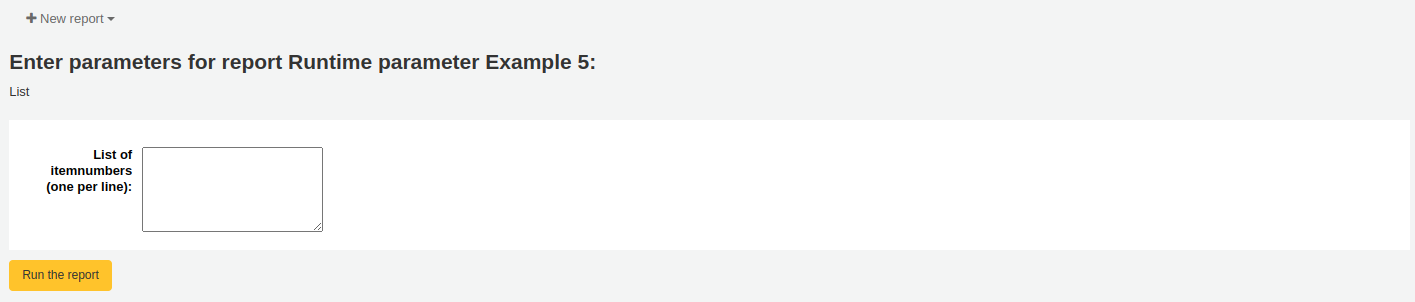
List: will display a large text box in which the user can enter many values, one per line. Those values will be inserted in the report, separated by commas, when it is run.
Warning
In the case of the list parameter, users must write one value per line.
Patron categories: will display a drop down menu of patron categories. The category code will be inserted in the report when it is run.
Cash registers: will display a drop down menu of cash registers. The cash register’s internal id will be inserted in the report when it is run.
Debit types: will display a drop down menu of debit types. The debit type code will be inserted in the report when it is run.
Credit types: will display a drop down menu of credit types. The credit type code will be inserted in the report when it is run.
Text field: will display an empty text field in which the user can enter any text.
Note
You have to put “%” in a text box to ‘leave it blank’. Otherwise, it literally looks for “” (empty string) as the value for the field.
For example entering nothing for: “title=<<Enter title>>” will display results with title=’’ (no title).
If you want to have to have something not mandatory, use “title like <<Enter title>>” and enter a % at run time instead of nothing.
After you choose the type of runtime parameter, it will ask you for the parameter label. This is what the user will see as the label for the choice they have to make or text they have to enter.
The syntax inserted into the report is <<Label|authorized_value>>.
The << and >> are just delimiters to indicate the start and end of the runtime parameter.
The label will be displayed on the left of the choice or value to enter.
The authorized_value can be omitted if not applicable. If it is absent, a free text field will be displayed. If it contains an authorized code (see table below), a drop down of the values will be displayed.
Note
You can write those in manually as well, you don’t have to go through the ‘Insert runtime parameter’ button. As long as the syntax is correct, Koha will interpret it as a runtime parameter.
List of parameters that can be used in runtime parameters
Parameter
What the user sees
What gets inserted in query
date
date picker
validly formatted date
branches
drop down of branch names
branch code
itemtypes
drop down of item type names
item type
categorycode
drop down of patron category descriptions
borrower category code
biblio_framework
drop down of MARC bibliographic frameworks
framework code
list
large text box
comma separated values
(auth-value-category)
drop down of auth-value descriptions in category
authorized value
(nothing)
text box
entered text
Note
You can have more than one runtime parameter in a given SQL query.
Note
When using runtime parameters that create drop down menus you can optionally specify whether to include an option for ‘All’ or to allow multiple selections.
To include an option for all the syntax is LIKE <<Label|branches:all>>.
To allow multiple selections the syntax is IN <<Label|itemtypes:in>>.
Example 1

Example 2
Example 3
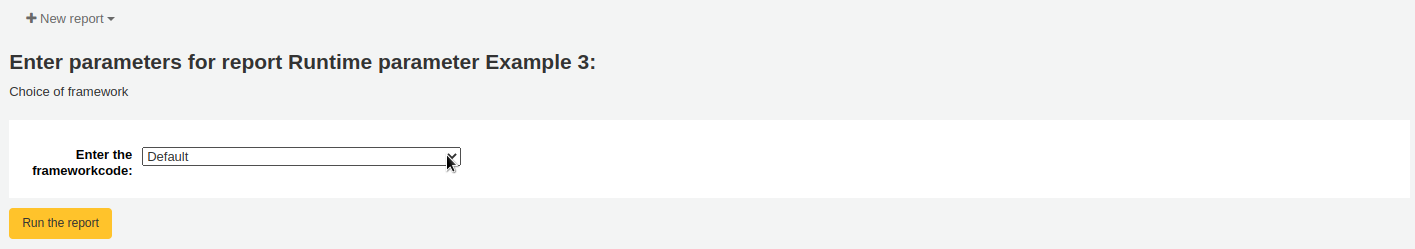
Example 4
Example 5
Warning
In the case of the list parameter, users must write one value per line.
You can use an SQL alias to rename columns.
Example
For reports whose results you wish to send to batch modification tools or generate automatic hyperlinks to use [[batch field|Column Name]] to rename the itemnumber, biblionumber or borrowernumber columns. For example, [[itemnumber|Item Number]] will format the itemnumber column as “Item Number”, while allowing those results to be sent to the batch item modification tool.
Example
It can be useful to add clickable links to reports to make it easier for staff to navigate directly to specific results.
Koha will automatically generate hyperlinks for any report that contains a borrowernumber, cardnumber, itemnumber or biblionumber.
Note
The column name must match the type of data your are inserting. Please see Column names for more details on naming columns for automatic hyperlinks.
When a user clicks on the number, the menu will prompt the user to click which Koha page they wish to visit.
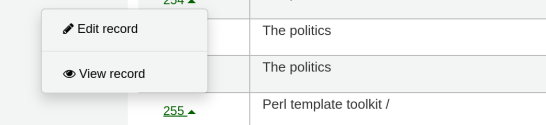
Available actions for each automatic link are:
borrowernumber: View, edit, check out
cardnumber: Check out
itemnumber: View, edit
biblionumber: View, edit
You may wish to make this a single click by directly linking to a specific page, or you may wish to make other data into clickable links; to make a book’s title a clickable link that brings the user to the bibliographic record, for example. Koha will insert HTML links added to the SELECT statement and by using CONCAT, data from the report results can be added to create a clickable link.
Example 1
This example uses the string /cgi-bin/koha/members/boraccount.pl?borrowernumber=XXXX to insert a direct link to a borrower. The end user will see the borrower’s library barcode number.
Note
Koha will automatically insert your library’s top level domain when a user clicks the link, so only “cgi-bin” and onward is required.
Note
The example uses single quotation marks to separate the CONCAT segments, which are joined by commas. Below is a detailed explanation of the sections, each of which is separated by a comma:
CONCAT - This SQL command combines separate queries and strings into a single column. Parentheses will enclose the next entries.
'<a href="/cgi-bin/koha/members/boraccount.pl?borrowernumber=' - The beginning of an HTML link tag and Koha URL that points to a specific borrower. The single quotation marks ensure the string is printed literally. You must escape the double quotation marks with a backslash to ensure Koha interprets it literally rather than as part of the SQL.
borrowernumber - The borrower number from the database. This is not enclosed by single quotation marks because we wish to query Koha.
'">' - The end of an opening HTML tag for a link. Again wrapped in single quotation marks.
cardnumber - The borrower’s barcode number queried from Koha. This is what will be visible to the user and comprise the clickable link.
'</a>' - A closing tag of an HTML link. Wrapped in single quotation marks.
Example 2
This example will link directly to an item, displaying the item’s barcode to the user.
Example 3
This example will link to a bibliographic record and display the item’s title.
In the “Create report from SQL”, you can search Mana KB for pre-made reports by clicking on “New report” and choosing “New SQL from Mana”.
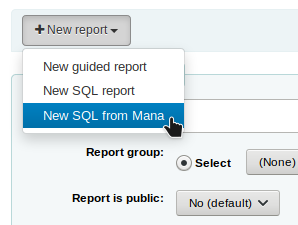
Note
This option will only appear if you’ve configured Mana KB in the administration module.
You will be prompted to enter keywords to search the knowledge base.
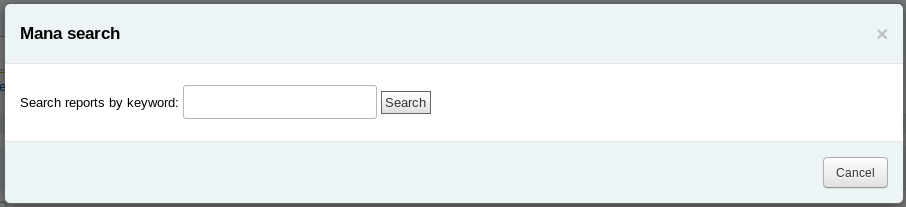
In the search results, you will see
the details of the report (name, notes and type)
how many people have used this entry (# of users)
when it was used for the last time (last import)
additional comments made by other Koha users (comments)
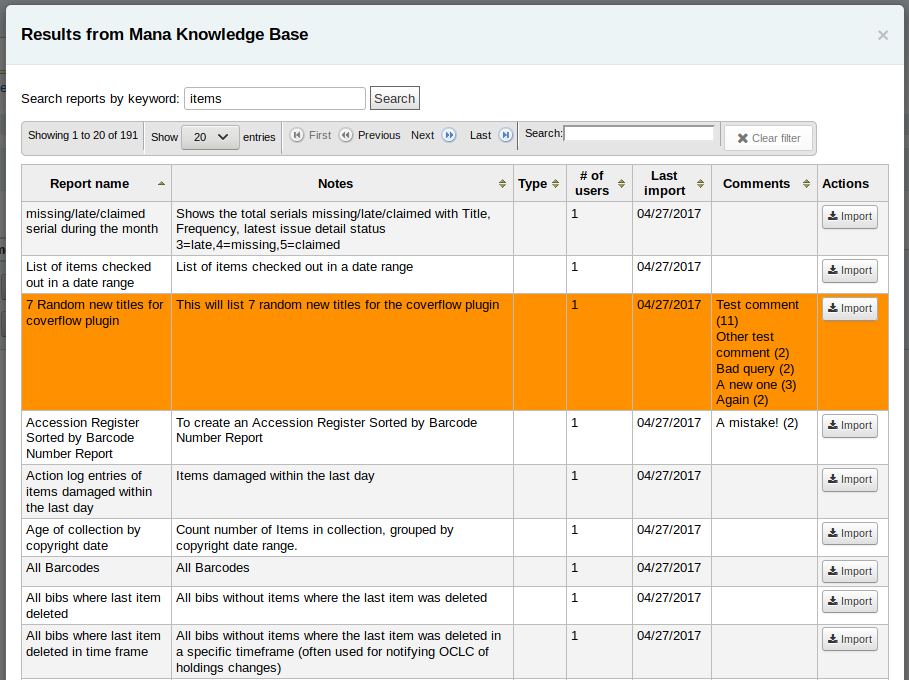
Click on “Import” to import a copy of the report in your own saved reports.
You can then edit it, duplicate it, delete it, run it as you would any of your own reports.
Duplicate reportReports can also be added by duplicating an existing report. Visit the ‘Saved reports’ page to see all of the reports listed on your system already.
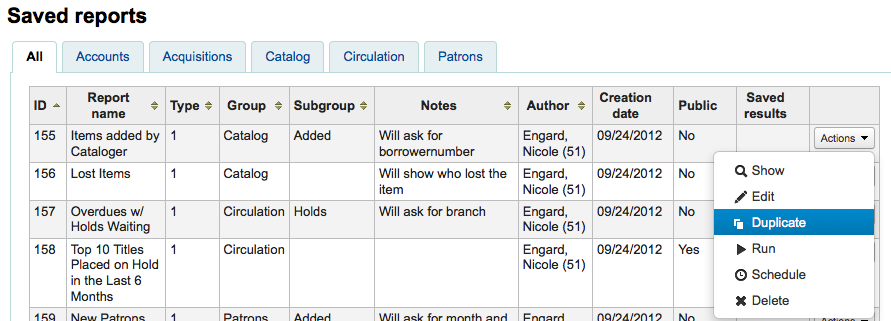
To the right of every report there is an ‘Actions’ pull down. Clicking that and choose ‘Duplicate’ to use an existing report as the basis for your new report. That will populate the new report form with the existing SQL for easy editing and resaving.
Edit custom reportsEvery report can be edited from the reports lists. To see the list of reports already stored in Koha, click ‘Use saved.’

Note
You can customize the columns of this table in the ‘Table settings’ section of the Administration module (table id: table_reports).
To find the report you’d like to edit you can sort by any of the columns by clicking the on the column header. You can also filter your results using the filter menu on the left or use the tabs to find reports based on your custom groups.
From this list you can edit any custom report by clicking ‘Actions’ to the right of the report and choosing ‘Edit’ from the menu that appears.
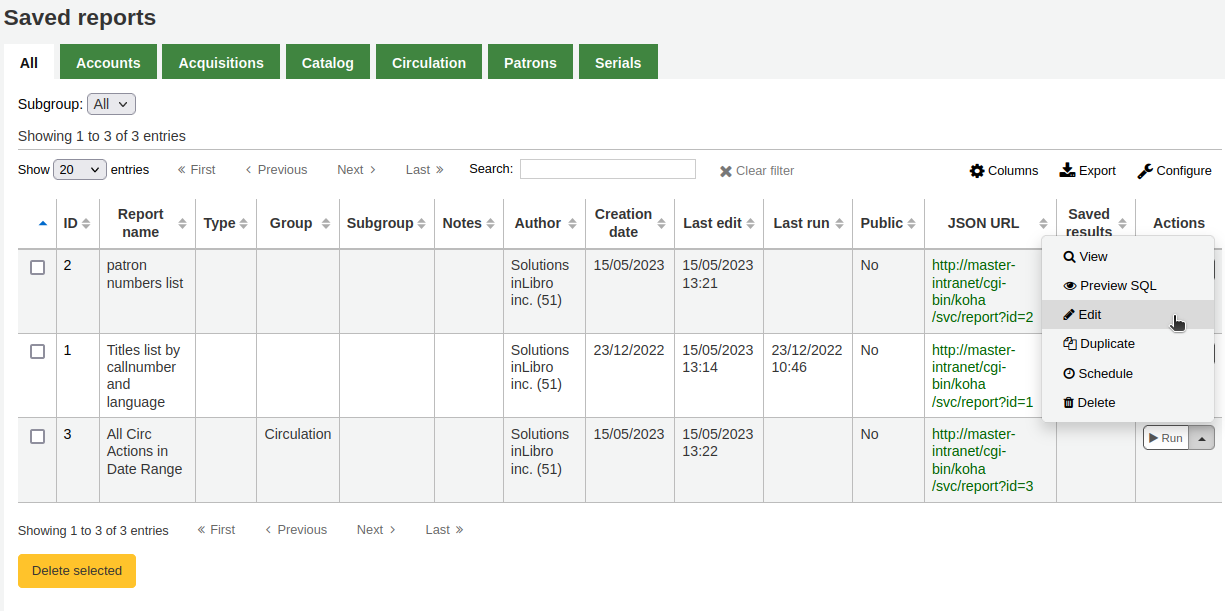
The form to edit the report will appear. Use the “update button” to save your modifications or click on “update and run SQL” to save and display the report results.
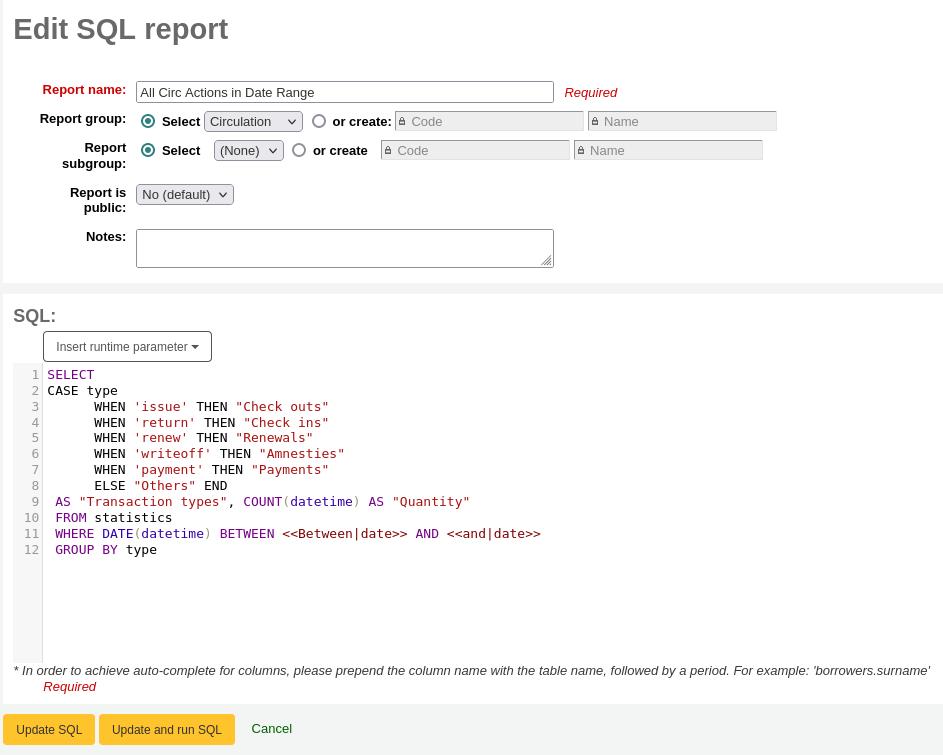
Note
Only staff with the execute_reports permission (or the superlibrarian permission) will be able to run existing reports.
Once custom reports are saved to Koha, you can run them by going to the Saved Reports page and clicking the ‘Run’ button to the right of the report.

When your report runs, you will either be asked for some values,

or you will see the results right away.
From the results you can do various actions with the button bar at the top of the page.
New report: create a brand new report.
New guided report: goes to the guided report wizard
New SQL report: goes to the create from SQL section
New SQL from Mana: this option only appears if Mana is set up, to search Mana for an existing SQL report.
Edit:
Edit: edit the current report
Duplicate: create a new report from the existing one
Delete: delete the current report
Run report: rerun the report
Run with template: this button only appears if you have notice templates in the notices and slips tool that are for reports.
Version
This option was added to Koha in version 23.11.
Tip
To view the results in a format other than the traditional table, you can create a template in the notices and slips tool.
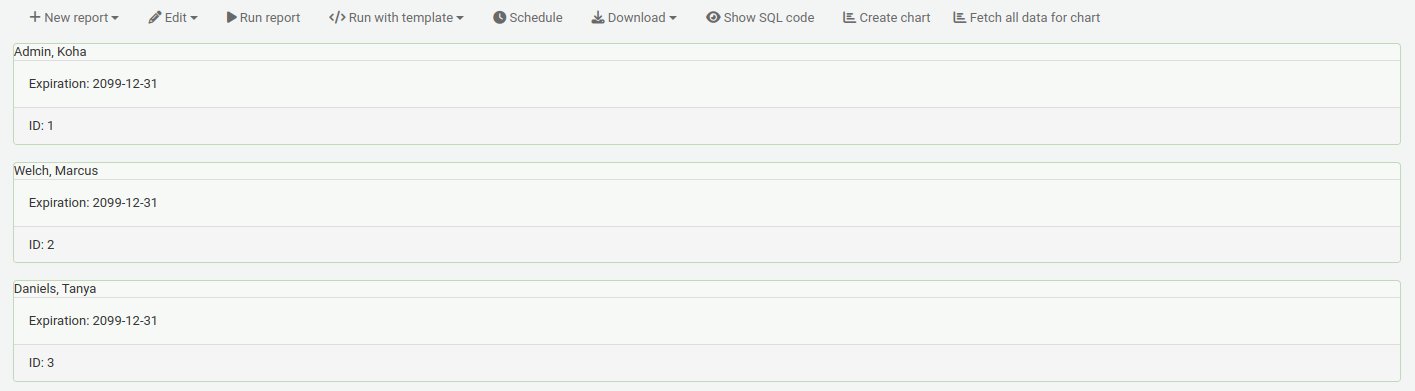
For example, to view patron information in ‘card’ form,
Go to Tools > Notices and slips.
Click ‘New notice’, and choose ‘Reports’.
Fill out the code and name for the slip. The name will be what appears in the ‘Run with template’ menu.
In the ‘Print’ template section, paste the code:
Click ‘Save’.
In a report with patron information, for example,
Click ‘Run with template’ and choose the template.
Instead of a table, the results will appear in ‘card’ form.
Schedule: schedule the report to be run at a later time with the task scheduler tool
Download: download the results
Comma separated text (.csv): a comma separated text file is a CSV file and it can be opened by any spreadsheet application or a text editor
Tab separated text: a tab separated text can also be opened by any spreadsheet or a text editor
Open Document Spreadsheet: ODS is an open-source spreadsheet file that can be opened in most spreadsheet applications
Rendered template: this option only appears if there are notice templates in the notices and slips tool that are for reports, and the report was “run with template” (see above). It allows you to download the report results with the template applied.
Version
This option was added to Koha in version 23.11.
Show SQL code: show the SQL query used to get those results
Create chart: create a pie chart or a line/bar chart with the visible results
Fetch all data for chart: make all the data visible to make a chart with all the data
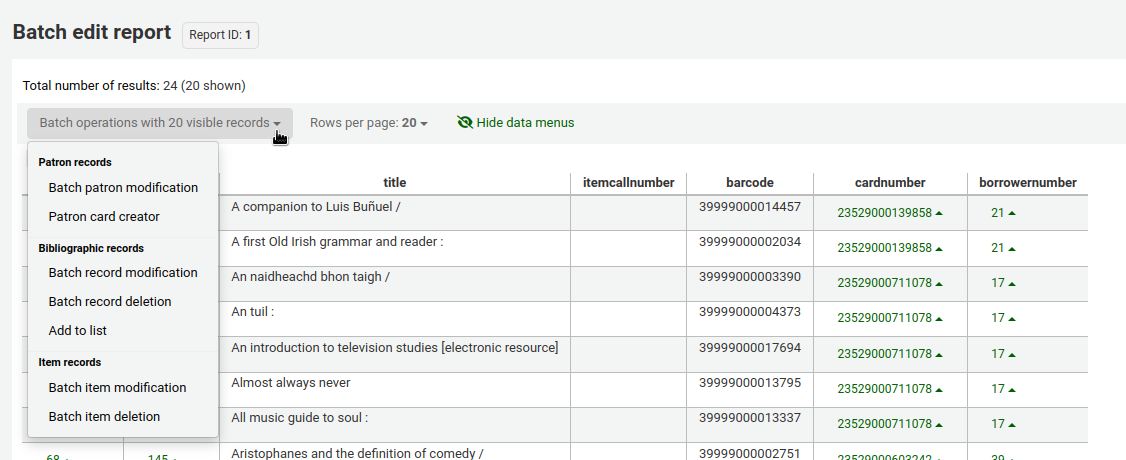
Send report output to batch modification toolsAfter running a report that contains itemnumbers, biblionumbers and/or patron cardnumbers the list of numbers can be imported directly into the relevant batch modification tool by clicking the ‘Batch operations with X visible records’ button in the report results. The X depends on the number of records you have chosen to display on screen (up to 1000).